What is Yellowfin Tuna "Ahi tuna" ?

Yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) also known as “Ahi tuna”; Is a Hawaiian name for yellowfin tuna that is often used in sushi and poke dishes. It is a species of tuna that is widely distributed in the world's oceans, particularly in tropical and subtropical waters. It is a highly migratory species that can be found in the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific oceans.
Yellowfin tuna is characterized by its sleek, torpedo-shaped body and metallic blue-black back, with yellow finlets and a yellow stripe on the side. It can grow up to 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) in length and weigh up to 440 pounds (200 kilograms).
Yellowfin tuna is a popular fish for commercial and recreational fishing due to its firm and flavorful meat. It is also commonly used in sushi and sashimi dishes. However, overfishing has led to a decline in yellowfin tuna populations in some areas, and efforts are being made to manage the fishery sustainably.
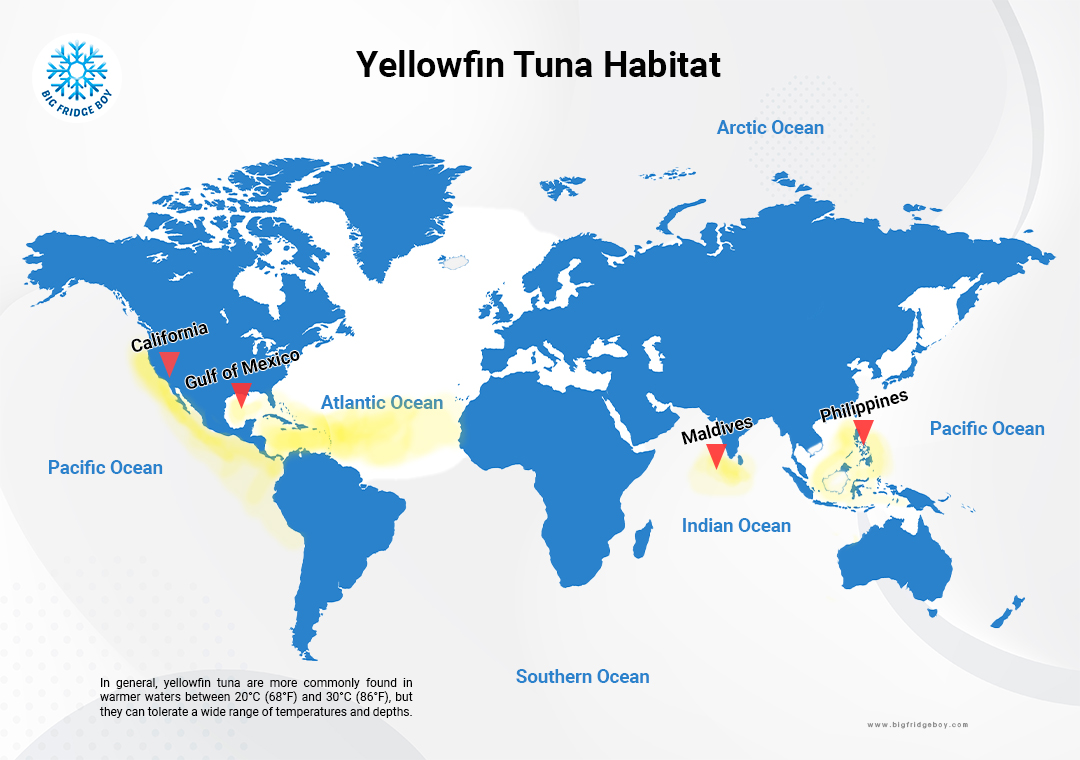
Habitat
Yellowfin tuna is a highly migratory species that are found in tropical and subtropical waters around the world. They inhabit the open ocean and are often found in association with floating objects such as logs, seaweed, or debris, as well as with dolphins, whales, and other large marine animals. Yellowfin tuna are found in all of the world's oceans, including the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans, and their distribution can vary depending on the time of year, ocean currents, and water temperature. In general, yellowfin tuna are more commonly found in warmer waters between 20°C (68°F) and 30°C (86°F), but they can tolerate a wide range of temperatures and depths.
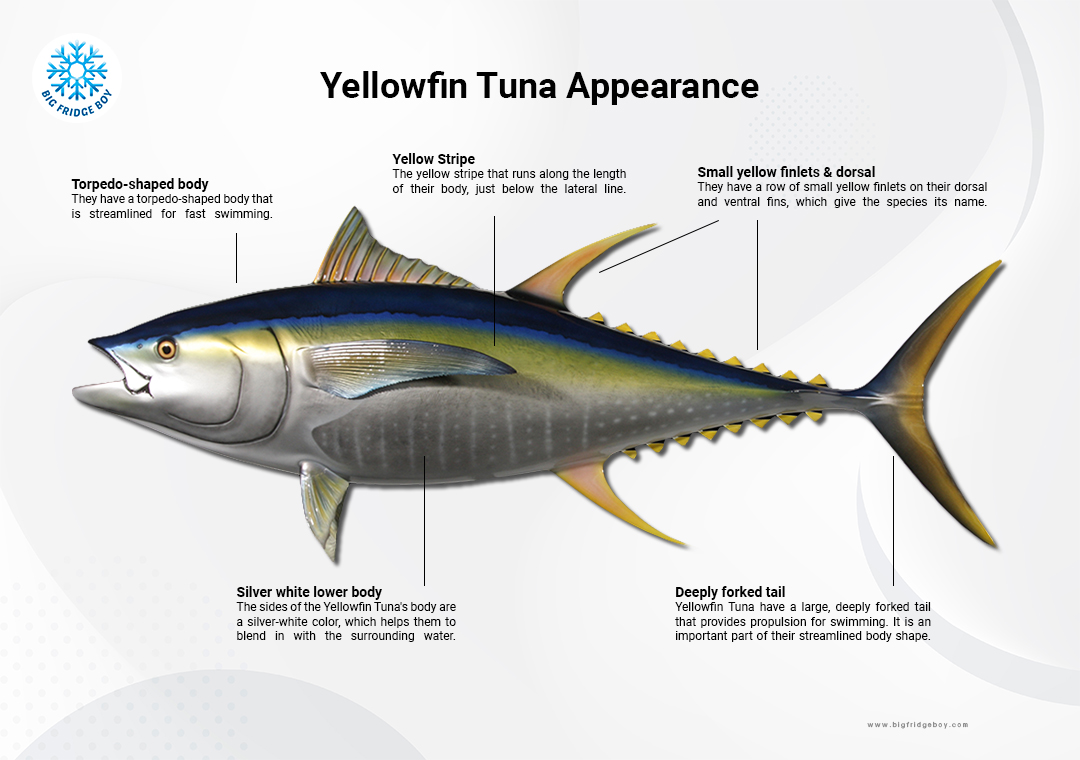
Appearance
Yellowfin tuna have a distinctive and sleek appearance that is characteristic of most tuna species. They have a torpedo-shaped body that is streamlined for fast swimming, with a pointed snout and a deeply forked tail.
The upper body of a yellowfin tuna is typically a metallic blue-black color, while the lower body is silver-white. They have a row of small yellow finlets on their dorsal and ventral fins, which give the species its name. In addition, yellowfin tuna have a yellow stripe that runs along the length of their body, just below the lateral line.
Yellowfin tuna is a relatively large species of tuna, with individuals typically ranging from 3 to 6 feet (1 to 1.8 meters) in length and weighing between 100 and 400 pounds (45 to 180 kilograms). However, some exceptionally large individuals can grow up to 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) in length and weigh up to 440 pounds (200 kilograms).
Diet
Yellowfin tuna are predatory fish that feed on a variety of small fish and invertebrates, depending on what is available in their environment. Their diet can vary depending on their life stage and location, but some common prey items for yellowfin tuna such as Squid Flying fish Sardines Anchovies Mackerel Crustaceans, such as krill and shrimp
Yellowfin tuna are active hunters that use their speed and agility to catch prey in open water. They are known for their ability to school with other tuna and form feeding frenzies where they chase and capture large schools of smaller fish. Yellowfin tuna also have excellent vision and can detect movement from a long distance, which helps them locate prey in the open ocean.
Lifespan
Yellowfin tuna have a relatively short lifespan compared to some other large fish species, with individuals typically living for 6 to 7 years on average. However, some individuals have been known to live for up to 8 to 10 years under favorable conditions.
Peak season
Yellowfin tuna can be found in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide, and they are generally available year-round. However, their availability and quality can vary depending on the region and season. In some areas, yellowfin tuna is considered to be at their best during specific seasons:
- Eastern Pacific Ocean: In the eastern Pacific, from Baja California down to Central and South America, yellowfin tuna are often more abundant during the warmer months, from June to October.
- Western Pacific Ocean: In the western Pacific, around the Philippines, Indonesia, and other parts of Southeast Asia, yellowfin tuna are more abundant during the transition from the northeast monsoon to the southwest monsoon, typically from March to June.
- Indian Ocean: In the Indian Ocean, the best season for yellowfin tuna can vary depending on the location. In the Maldives, for example, yellowfin tuna are more abundant during the southwest monsoon season, from May to October.
- Atlantic Ocean: In the Atlantic, yellowfin tuna can be found year-round, but their availability might vary depending on the region. In the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean, yellowfin tuna are generally more abundant from April to November.
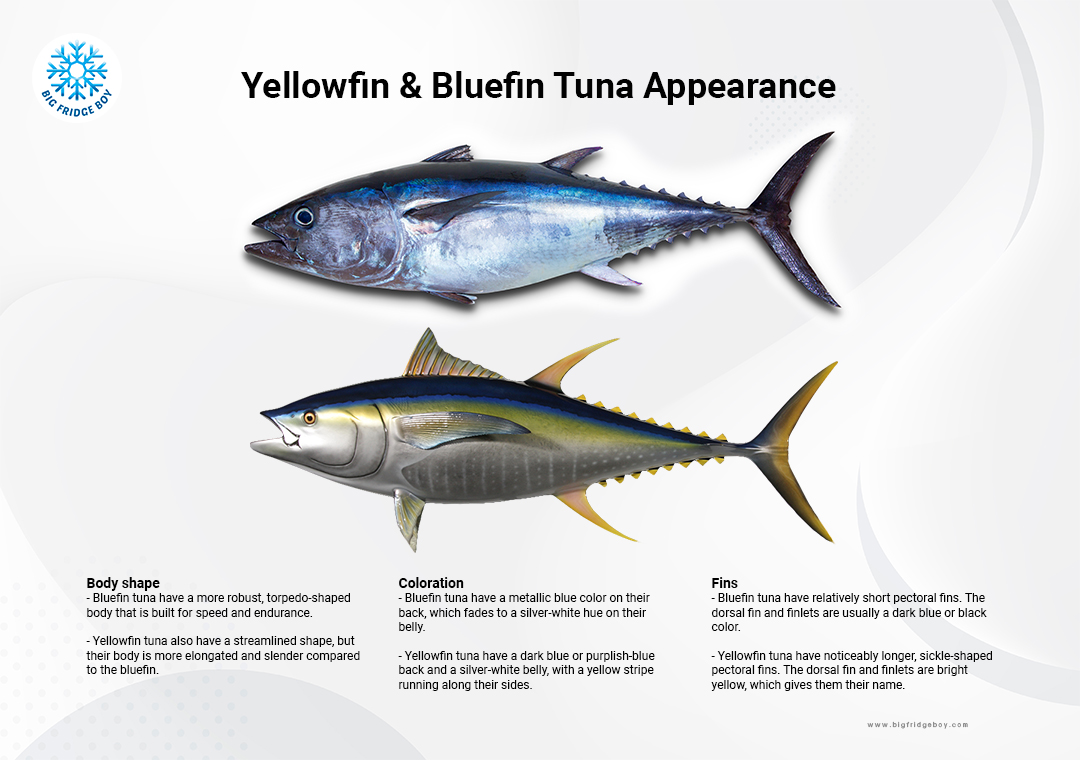
Bluefin Tuna vs Yellowfin Tuna
Bluefin and yellowfin tuna are very different from one another in terms of their look, habitat, culinary applications, and cost. Here is a list of the main distinctions:
- Body shape
- Bluefin tuna have a more robust, torpedo-shaped body that is built for speed and endurance.
- Yellowfin tuna also have a streamlined shape, but their body is more elongated and slender compared to the bluefin. - Coloration
- Bluefin tuna have a metallic blue color on their back, which fades to a silver-white hue on their belly.
- Yellowfin tuna have a dark blue or purplish-blue back and a silver-white belly, with a yellow stripe running along their sides. - Fins
- Bluefin tuna have relatively short pectoral fins. The dorsal fin and finlets are usually a dark blue or black color.
- Yellowfin tuna have noticeably longer, sickle-shaped pectoral fins. The dorsal fin and finlets are bright yellow, which gives them their name. - Size
Bluefin tuna are generally larger than yellowfin tuna.
- The Atlantic bluefin tuna can grow up to 15 feet (4.6 meters) in length and weigh over 1,500 pounds (680 kg). Pacific bluefin tuna can grow up to 9.8 feet (3 meters) and weigh around 990 pounds (450 kg).
- Yellowfin tuna typically grow up to 7.5 feet (2.3 meters) in length and can weigh up to 440 pounds (200 kg).
Compared to bluefin tuna. Yellowfin tuna is a fish that lives in warmer waters. The texture and taste are milder. But can be bought easily and cheaply, which is another option that is not less interesting. For a variety of cooking.
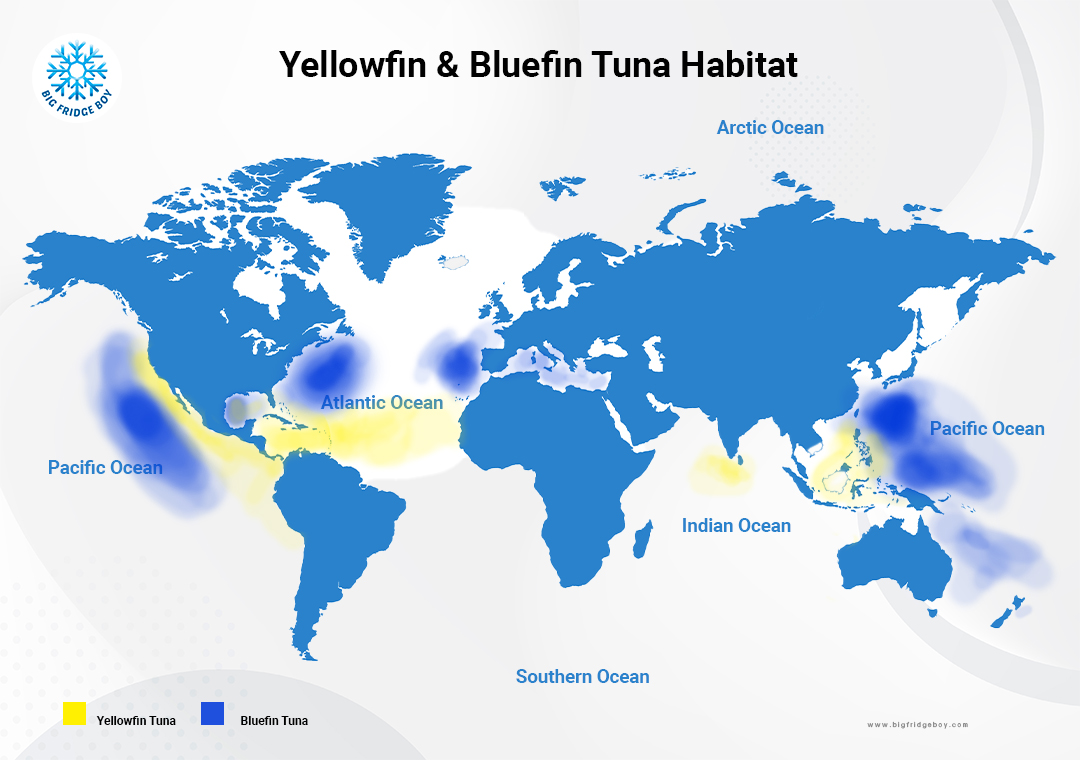
- Habitat preferences
- Bluefin tuna prefer cooler waters and are typically found in temperate and cold waters of the Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, and some parts of the Pacific Ocean.
- Yellowfin tuna inhabit tropical and subtropical waters worldwide, including the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. - Culinary uses
- Bluefin tuna has a high price, excellent quality, and high fat content, especially the fat belly called otoro or chutoro. It is the most expensive part because of the intense flavor and tender texture that melts in the mouth. It is often eaten raw as sushi and sashimi. or only through a small amount of cooking in order to fully enhance the natural flavor of the fish.
- Yellowfin tuna has a cheaper price. It has a slightly milder taste. Less fat but a firm texture can be eaten raw, as sushi or sashimi, for example. But it is often used in pre-seasoned dishes such as poke bowls, a popular sushi salad. Or it may be packaged in cans as canned tuna. Therefore, it is another option at a more affordable price.
Yellowfin tuna It is a fish that lives in warmer waters. Bluefin tuna is easily available and cheaper, although the taste and texture may not be comparable to those of bluefin tuna. But it's an interesting option for a variety of cuisines.







